Methylation - Particularly as it Applies to Gout
Anonymous has been looking into the association between MTHFR and gout. This may be a productive new avenue to explore and I'm going to put links and theory under this category on this page.
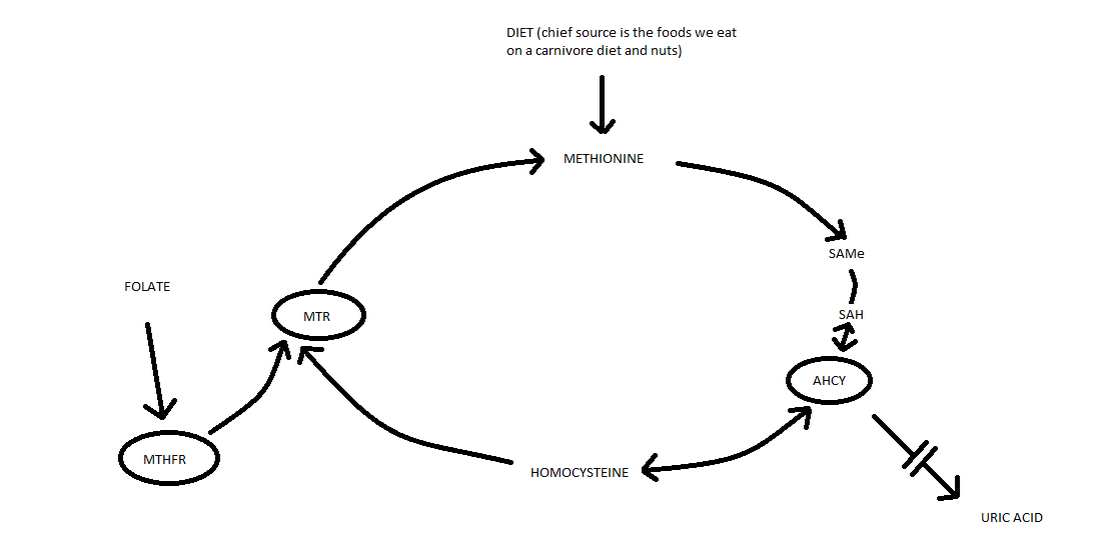
In VERY simple terms: The methylation cycle converts homocysteine into methionine which is then used to make the methyl donor SAMe. Once the methyl group has been donated, we are left with S Adenosine Homocysteine (SAH) which is then converted to homocysteine.
For many people (mostly of European descent) this cycle does not work properly due to several mutations in the MTHFR gene. The MTHFR mutations result in a reduction in the amount of the active form of folate L-F-MTHF which in turn inhibits the activity of the MTR gene and results in a build-up of homocysteine. This build-up of homocysteine can back feed to create more SAH which can “perhaps” lead to raised levels of uric acid.
It is worth noting that many people switching to a carnivore or zero carb diet will by default increase their consumption of foods containing methionine and hence could exasperate any existing issues with the methylation cycle and “potentially increase their risk of gout”.
See the 4-part Youtube series by Dr. Neil Rawlins for a good introduction into the MTHFR gene and its mutations.
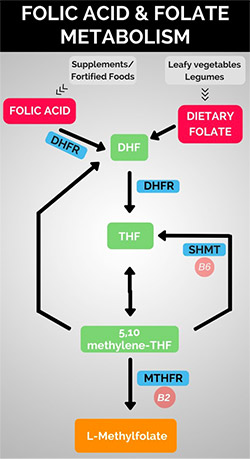
The man-made substance Folic Acid is now added to many foods. However, for those with MTHFR mutations this is a disaster as Folic Acid can block the receptors for the active form of folate L-5-MTHF.
Most people can successfully treat high homocysteine levels by taking L-5-MTHF supplements and Hydroxo or Methyl B12. Methylcobalamin (B12) is the other main input to the MTR gene.
See the work of Dr. Amy Yasko for more information on how to treat MTHFR issues. In his paper “Reversal of cognitive decline: A novel therapeutic program” Dr. Dale Bredesen recommends Methyl-B12, Methyl-Folate, P5P and if necessary TMG to treat high homocysteine levels.
For many people (mostly of European descent) this cycle does not work properly due to several mutations in the MTHFR gene. The MTHFR mutations result in a reduction in the amount of the active form of folate L-F-MTHF which in turn inhibits the activity of the MTR gene and results in a build-up of homocysteine. This build-up of homocysteine can back feed to create more SAH which can “perhaps” lead to raised levels of uric acid.
It is worth noting that many people switching to a carnivore or zero carb diet will by default increase their consumption of foods containing methionine and hence could exasperate any existing issues with the methylation cycle and “potentially increase their risk of gout”.
See the 4-part Youtube series by Dr. Neil Rawlins for a good introduction into the MTHFR gene and its mutations.
The man-made substance Folic Acid is now added to many foods. However, for those with MTHFR mutations this is a disaster as Folic Acid can block the receptors for the active form of folate L-5-MTHF.
Most people can successfully treat high homocysteine levels by taking L-5-MTHF supplements and Hydroxo or Methyl B12. Methylcobalamin (B12) is the other main input to the MTR gene.
See the work of Dr. Amy Yasko for more information on how to treat MTHFR issues. In his paper “Reversal of cognitive decline: A novel therapeutic program” Dr. Dale Bredesen recommends Methyl-B12, Methyl-Folate, P5P and if necessary TMG to treat high homocysteine levels.
More on Methylation
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| |||||||
Additionally, if there are aberrations or expressive genetic mutations in the body’s methylation cycles (such as MTHFR, MTRR, SUOX, CBS), this can alter the rate of purine and uric acid biosynthesis. The pathway to purine biosynthesis is induced from 5, 10 methylene tetrahydrofolate. This folate metabolite is directly affected by multiple methylation reactions, involving many enzymes. Considering the high prevalence of methylation cycle dysfunction, one should always give attention to this factor when uric acid is elevated. Methylation dysfunction may be a core component of cardiovascular disease because of methylation’s role in homocysteine metabolism, glutathione formation and nitric oxide synthesis. |
Although folate occurs in naturally in some foods, and folic acid is used to fortify others, approximately 60 percent of the population in the United States have genetic variations that make them unable to utilize these nutrients. These variations do not allow the MTHFR enzyme to function properly so methylation of folate does not occur. Without this activation step, folate cannot be used by the body, resulting in negative health side effects and the possible inability to maintain a healthy mood. |
Methylation, choline and the link with fatty liver and a carnivore based diet.