Vitamin D
Vitamin D is responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate. In general, vitamin D functions to activate the innate and dampen the adaptive immune systems. (Study: Vitamin D and the immune system: new perspectives on an old theme "It is thus tempting to speculate that effects of vitamin D on this disease may involve both the activation of innate immunity, together with the suppression of adaptive immunity and associated inflammation.")
My Story
Back around 2002 I took up golf and have played it an average of 3 days a week for the last 15 years. Prior to that I was accustomed to getting 2 or more episodes of a cold or flu each year. The last 15 years have seen me with no colds or flu whatsoever. What is this strange link between golf and immunity to colds?
My conclusion has been that it must be related to the sunshine I'm getting on such a regular basis throughout the year. This has been backed up by the research I've done on the benefits of vitamin D and much of which I've linked to below.
Read on to find out more of the potential benefits of getting out in the sun more often - or supplementing if that is difficult.
Back around 2002 I took up golf and have played it an average of 3 days a week for the last 15 years. Prior to that I was accustomed to getting 2 or more episodes of a cold or flu each year. The last 15 years have seen me with no colds or flu whatsoever. What is this strange link between golf and immunity to colds?
My conclusion has been that it must be related to the sunshine I'm getting on such a regular basis throughout the year. This has been backed up by the research I've done on the benefits of vitamin D and much of which I've linked to below.
Read on to find out more of the potential benefits of getting out in the sun more often - or supplementing if that is difficult.
I recently had a section here on Vitamin D as it relates to Covid19 but have moved the studies and links to a separate page here.
Stop press... recent meta analysis shows definitive benefit of vitamin D in preventing hospitalisation and mortality of people with Covid19
Stop press... recent meta analysis shows definitive benefit of vitamin D in preventing hospitalisation and mortality of people with Covid19
How important is Vitamin D?
Sunlight and Vitamin D: Necessary for Public Health - Journal of the American College of Nutrition
The World Health Organization's International Agency for Research on Cancer recommends avoiding outdoor activities at midday, wearing clothing to cover the whole body, and daily use of sunscreen on usually exposed skin. The American Cancer Society advocates Slip! Slop! Slap! and Wrap! to make sure skin is covered in clothing or sunscreen and to avoid exposure to the sun between 10 am and 4 pm. The U.S. Surgeon General has issued a Call to Action focused on reducing ultraviolet (UV) exposure, whether from indoor UV or from the sun. Though these recommendations, all focused on reduction of skin cancer, are accompanied by brief acknowledgement of the importance of vitamin D for health, they persist in urging avoidance of the sun at the precise times when vitamin D can be synthesized in the skin—the hours between 10 am and 3 pm—and suggest that all necessary vitamin D can be obtained through food and dietary supplements.
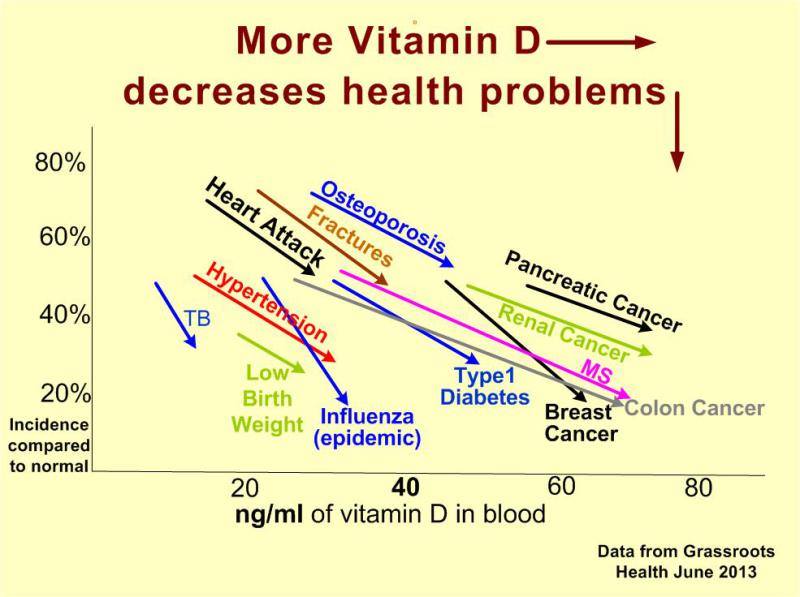
These recommendations are understandable from the viewpoint of preventing the 3.5 million new cases of and 2000 deaths from nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States each year, but they neglect the fact that we have a long cultural history of appreciation of the sun and use of UV radiation for healing purposes. Moreover, they neglect that we have evolved with physiological adaptations to help protect the skin from the sun when we are mindful of our exposure and do not burn. They neglect the fact that increased sun exposure, based on latitude, has been associated with protection from several different types of cancer, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and other diseases. They also neglect the fact that exposure to the sun induces beneficial physiological changes beyond the production of vitamin D. Though adherence to the current sun-protective recommendations would likely result in the reduction of nonmelanoma skin cancer, that reduction would likely be overshadowed by the potential reduction in deaths from other cancers and from cardiovascular disease, which could be achieved by doubling average blood concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) to 40 ng/mL through a combination of sun exposure and supplements.
Sunlight and Vitamin D: Necessary for Public Health - Journal of the American College of Nutrition
The World Health Organization's International Agency for Research on Cancer recommends avoiding outdoor activities at midday, wearing clothing to cover the whole body, and daily use of sunscreen on usually exposed skin. The American Cancer Society advocates Slip! Slop! Slap! and Wrap! to make sure skin is covered in clothing or sunscreen and to avoid exposure to the sun between 10 am and 4 pm. The U.S. Surgeon General has issued a Call to Action focused on reducing ultraviolet (UV) exposure, whether from indoor UV or from the sun. Though these recommendations, all focused on reduction of skin cancer, are accompanied by brief acknowledgement of the importance of vitamin D for health, they persist in urging avoidance of the sun at the precise times when vitamin D can be synthesized in the skin—the hours between 10 am and 3 pm—and suggest that all necessary vitamin D can be obtained through food and dietary supplements.
These recommendations are understandable from the viewpoint of preventing the 3.5 million new cases of and 2000 deaths from nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States each year, but they neglect the fact that we have a long cultural history of appreciation of the sun and use of UV radiation for healing purposes. Moreover, they neglect that we have evolved with physiological adaptations to help protect the skin from the sun when we are mindful of our exposure and do not burn. They neglect the fact that increased sun exposure, based on latitude, has been associated with protection from several different types of cancer, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and other diseases. They also neglect the fact that exposure to the sun induces beneficial physiological changes beyond the production of vitamin D. Though adherence to the current sun-protective recommendations would likely result in the reduction of nonmelanoma skin cancer, that reduction would likely be overshadowed by the potential reduction in deaths from other cancers and from cardiovascular disease, which could be achieved by doubling average blood concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) to 40 ng/mL through a combination of sun exposure and supplements.
For Those Who Like to Watch Video Lectures
|
|
This is the first video on this page and the one I would recommend to watch first. Here is a professor (Cedric F. Garland), talking about what he has found regarding its protective effect against various cancers
| |||||||
|
|
Ivor Cummins on Vitamin D from an engineer's perspective. "Leveraging the knowledge of the foremost experts in the field, I can now release what I believe is a comprehensive explanation of the Vitamin D story. It's benefits are difficult to disentangle from those of healthy Sun Exposure though - the beneficial effects of D status may be hugely due to the sun exposure that got your D up! I use sun and UV sources to achieve my D levels as a result, not supplementation. Other key elements like K2, A, Mg etc are inextricably linked also, but here we focus mainly on D. Reverse Causality applies also - people who have inflammatory issues and are obese may drive down their D status, but data on this is sparse - but keep it in mind. Also important is that DAILY supplementation rather than big bolus dosing is used - the half-life of D3 is only a couple of days. This Seminar is of interest to Mothers & their Children particularly (e.g. see 15:00:00 to 21:00:00 segment), to avoid probability of serious chronic diseases, in childhood and beyond. The main message is that blood levels of D should be targeted towards healthy evolutionary levels, ideally through access to UVB / healthy sun exposure (NO burning). So to stress again: there is a lot of associational "correlation but possibly not causation" data in this, and there is every possibility that Sun exposure delivers more benefits than D3 supplements (by the production of many other photoproducts in the skin), and also the modern carb-inflamed/diseased population may be causal in driving down 25(OH)D status (e.g. the obese people with low D - is it their fat sequestering away the D, or is their inflammation driving down their status?) Anyway, thanks for watching! Ivor Cummins BE(Chem), CEng MIEI Slides from 'D is for Debacle |
|
|
Christopher Sorli gives a very good lecture showing the data that relates to vitamin d3 benefits and dosages |
|
|
Michael Holick talks about sunlight and its effects on our physiology |
|
|
Bruce Hollis PhD discusses results of a Prostate Cancer/Vitamin D Trial: Effectiveness Safety Recommendations
|
How Does it All Work?
Post by Raymund Edwards
Vitamin D functions within two systems in the human body:
Post by Raymund Edwards
Vitamin D functions within two systems in the human body:
- The endocrine system - maintains calcium homeostasis and bone health. This system uses the metabolized form of vitamin D called 25(OH)D and by the time it is turned into 1,25(OH)2D, the usable form, it has a half life of three weeks. All the studies on bone health have been successful based on dosage, not frequency, because of this long half life.
- The autocrine/paracrine system - vitamin D is delivered to non-skeletal systems such as breast, colon, and prostate tissues and helps affect autoimmune disorders, cancer, cardiovascular disease and infections. In this system, vitamin D goes into a cell and helps regulate cell growth, after this process vitamin D has a half life of 24 hours, meaning frequency of dosing matters when testing for disease reduction and immune control.
- Vitamin D3 enters the body through sun exposure, diet or a supplement and goes into the blood stream where it binds to the vitamin D binding protein (VDBP) -- a protein that carries vitamin D compounds into circulation. From there, vitamin D3 functions within two systems in the human body (the two systems mentioned above ).
- The first is the endocrine system, which maintains calcium homeostasis and bone health. In this system, vitamin D3 is transported to the liver where it is metabolized into 25(OH)D. The 25(OH)D along with the VDBP complex (binding protein) is then transported into the kidneys via a special active transport system--called the megalin-mediated system. The kidney's enzymes transform the compound into the active hormone 1,25(OH)2D, and the kidney then excretes 1,25(OH)2D back into the blood stream where the intestine helps facilitate calcium absorption--maintaining bone health.
- The second of these systems is the autocrine/paracrine system. Through these pathways, vitamin D3 is delivered to the majority of non-skeletal systems such as the breast, colon, skin, brain, ovary and prostate tissues. While vitamin D3 is transported through the blood stream, it breaks its bind from VDBP and enters the body's various cells via simple diffusion. Within the cell, enzymes metabolize the vitamin D3 to 25(OH)D and then to 1,25(OH)2D, which works to regulate cell growth and perform other helpful functions.
- Tissues in the autocrine/paracrine system are not equipped with the megalin-mediated transport system, so if vitamin D compounds are bound to the VDBP, they cannot enter these cells. Vitamin D3 binds loosely to the VDBP and can easily break off and enter the cells of the autocrine/paracrine system. Conversely, 25(OH)D binds very tightly to the VDBP and only a small amount is able to break free and enter these tissues. Therefore, vitamin D3 is needed for these non-skeletal systems.
- The length of time that a vitamin D compound stays in the blood is based on how tightly it is bound to the VDBP (the vitamin D binding protein). The 25(OH)D used in the endocrine system has a half life of three weeks because it is bound very tightly to the VDBP, while vitamin D3 used in the autocrine system has a half life of 24 hours. Therefore, a daily input is needed to maintain stable vitamin D3 levels for non-skeletal systems. For bone health, a weekly or even monthly intake would have a positive effect on the body.
- For example, if someone takes a large dose of vitamin D3 on a weekly basis, within a couple days all of the vitamin D3 is metabolized into 25(OH)D, which cannot get into the cells.. For the remaining five days until the next weekly dose, the body would have no detectable vitamin D3.
- Breast feeding mothers could have 50-60 ng/ml of measurable 25(OH)D in their blood but no measurable vitamin D3 in their breastmilk so dosing daily is important. After vitamin D3 has been turned to 25(OH)D it cannot enter the breast milk. The only way to get vitamin D in breastmilk is by dosing daily - either by sun, diet or supplementation. Dr. Hollis' research indicated that 6,400 IU/day was necessary for breast feeding mothers.
- Most of the clinical trials conducted in the past 40 years have focused on the endocrine system and have consistently shown the positive effects of vitamin D on bone health regardless of dosing regimen (from daily to quarterly). In the past 10 years, many new clinical trials have focused on non-skeletal outcomes such as autoimmune disorders, cancer, cardiovascular disease and infections. These new studies have also used various dosing regimens--but have yielded inconsistent results. Those with adequate daily vitamin D inputs have largely shown positive results while those with longer dosing intervals have shown no vitamin D effect. While 25(OH)D levels are maintained in these studies, it is the vitamin D3 levels that are essential to these systems. Therefore, it is necessary to design a clinical trial based on the physiology of the system of interest in order to accurately assess the effect of vitamin D in the body.
- +++++ >>> "Vitamin D intakes of up to 10,000 IU/per day and circulation 25(OH)D levels of up to 100 ng/ml (250 nmol) are normal in human physiology. Do not treat as poison." - Bruce Hollis
If people did nothing but take a meaningful daily amount of Vitamin D. |
Vitamin D Deficiency Linked More Closely to Diabetes than Obesity
People who have low levels of vitamin D are more likely to have diabetes, regardless of how much they weigh, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
ENDOCRINE.ORG
People who have low levels of vitamin D are more likely to have diabetes, regardless of how much they weigh, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
ENDOCRINE.ORG
From Edward Hutchinson
Over the last 50 years health professionals have been trying to persuade people to stay out of the sun and use high protection sunscreen.
Most people now have lower vitamin d levels than were common in previously and modern lifestyles lead to more time indoors or under cover (in cars)
Vitamin d regulates intestinal permeability, Leaky gut.
While it's true gluten promotes the production of zonulin, and Zonulin, is also involved in the regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3384703/ it's also the case that lower vitamin d levels also lead to intestinal permeability, leaky gut.
Tight junction CLDN2 gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4650691/
If we don't keep our 25(OH)D levels at or above 125nmol/l 50ng/ml with daily vitamin d3 or UVB exposure, we will not have freely bioavailable cholecalciferol present to maintain our endothelial barrier.
Dietary Vitamin D and Its Metabolites Non-Genomically Stabilize the Endothelium
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4607301/
Over the last 50 years health professionals have been trying to persuade people to stay out of the sun and use high protection sunscreen.
Most people now have lower vitamin d levels than were common in previously and modern lifestyles lead to more time indoors or under cover (in cars)
Vitamin d regulates intestinal permeability, Leaky gut.
While it's true gluten promotes the production of zonulin, and Zonulin, is also involved in the regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3384703/ it's also the case that lower vitamin d levels also lead to intestinal permeability, leaky gut.
Tight junction CLDN2 gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4650691/
If we don't keep our 25(OH)D levels at or above 125nmol/l 50ng/ml with daily vitamin d3 or UVB exposure, we will not have freely bioavailable cholecalciferol present to maintain our endothelial barrier.
Dietary Vitamin D and Its Metabolites Non-Genomically Stabilize the Endothelium
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4607301/
Vitamin D and Epilepsy
The anticonvulsive effect of vitamin D is now supported by evidence coming from different sources including ecological and clinical interventional studies as well as animal experiments. Several antiepileptic drugs, especially those with enzyme inducer properties, decrease vitamin D level which paradoxically may predispose to more seizures. These facts together with the worldwide problem of vitamin D deciency and the known relationship of insufcient vitamin D levels with the major disorders of civilization warrant routine screening and supplementation of vitamin D in epilepsy patients. Further studies are needed to more closely determine the optimal level of vitamin D from the epilepsy point of view.
Epilepsy and Vitamin D (PDF Download Available). Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257070539_Epilepsy_and_Vitamin_D [accessed Sep 27, 2017].
The anticonvulsive effect of vitamin D is now supported by evidence coming from different sources including ecological and clinical interventional studies as well as animal experiments. Several antiepileptic drugs, especially those with enzyme inducer properties, decrease vitamin D level which paradoxically may predispose to more seizures. These facts together with the worldwide problem of vitamin D deciency and the known relationship of insufcient vitamin D levels with the major disorders of civilization warrant routine screening and supplementation of vitamin D in epilepsy patients. Further studies are needed to more closely determine the optimal level of vitamin D from the epilepsy point of view.
Epilepsy and Vitamin D (PDF Download Available). Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257070539_Epilepsy_and_Vitamin_D [accessed Sep 27, 2017].
General Links to Vitamin D Articles
- Efficacy of vitamin D3 supplementation on cancer mortality: Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials - June - 2023
This systematic review and IPD meta-analysis observed that, overall, vitamin D3 supplementation resulted in a statistically non-significant 6% reduction of cancer mortality in the general population, 5% improved overall survival of cancer patients and 7% improved cancer-specific survival of cancer patients. The relationship with cancer mortality was stronger and statistically significant when the analysis was restricted to trials with a daily vitamin D3 dosing regimen (reduction by 12%). - Regular use of vitamin D supplement is associated with fewer melanoma cases compared to non-use: a cross-sectional study in 498 adult subjects at risk of skin cancers - December, 2022
- Vitamin D supplements reduce the risk of dynapenia in older people by 78% - 13 December, 2022
"we found that the risk of developing muscle weakness by the end of the four-year period was 78% higher for subjects with vitamin D deficiency at the start of the study than for subjects with normal vitamin D levels and 77% higher for those with vitamin D insufficiency [30-50 nmol/L]" - Brain vitamin D forms, cognitive decline, and neuropathology in community-dwelling older adults - 7 December 2022
Higher brain 25(OH)D3 concentrations were associated with better cognitive function prior to death. Additional research is needed to clarify the specific mechanisms underlying this potentially protective relationship. - Vitamin D supplementation is associated with slower epigenetic aging - 13 May, 2022
Previous research has shown that vitamin D deficiency is associated with accelerated aging.
In this new study, the same researchers found that supplementing with vitamin D showed a 2.6-year lower “age score” compared to those who did not supplement with vitamin D and those who were still deficient in vitamin D. That’s no small effect—and it’s a big deal because some surveys suggest that up to 92% of Americans are vitamin D deficient. - Vitamin D and marine omega 3 fatty acid supplementation and incident autoimmune disease: VITAL randomized controlled trial
- Vitamin D for All to Prevent MS?
- Second Opinions (Barry Groves) on Skin Cancer
(Some people have a hard time accessing this site so I've created copies of the parts here: Part 1; Part 2; Part 3; Part 4; Part 5) - Sunscreen and Melanoma: Is Our Prevention Message Correct?
- Vitamin D as a Therapeutic Option for Sunburn: Clinical and Biologic Implications
"In a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled pilot study, out group recently demonstrated that vitamin D3 reduces skin inflammation when administered to humans 1 h after sunburn." - The roles of UVB and vitamin D in reducing risk of cancer incidence and mortality:
A review of the epidemiology, clinical trials, and mechanisms. - Vitamin D – Why You are Probably NOT Getting Enough - Mark Hyman MD
- Does Sufficient Evidence Exist to Support a Causal Association between Vitamin D Status and Cardiovascular Disease Risk? An Assessment Using Hill’s Criteria for Causality
- Effects of high doses of vitamin D3 on mucosa-associated gut microbiome vary between regions of the human gastrointestinal tract
- Daily recommended doses of vitamin D are based on a mathmatical error and are too low
- The Big Vitamin D Mistake - Higher Prevalence of Type 1 Diabetes in Finland
- Jenn Millar has written a great article on 15 benefits of vitamin D and the best foods to get it from here
- Csaba Tóth and Zsófia Clemens feel that adequate levels of vitamin D can be obtained through nutrition alone
However, they cite only two studies which indicate only that people living on traditional diets in cold countries have greater levels of D than do their countrymen who have switched to more modern diets. This does not speak to whether the levels experienced in the traditional dieters are adequate to give optimal health. They claim that adequate levels can be obtained by nutrition alone, based on opinion and a couple of studies, without taking into consideration that people living on traditional diets might well have even better immunity if they had more access to year round sunlight as well as their diets. They may well still be sub-optimal when compared to people living near the equator on their traditional diets.
On the other hand, there are some 4,620 studies published on vitamin D in the 12 months up to August 2018 adding to some 77, 322 studies held by the US National Library of Medicine. - Vitamin D and Health - Harvard School of Public Health
This one mentions the studies on bone health in the elderly and the ineffectiveness of lower doses of D
"Several studies link low vitamin D levels with an increased risk of fractures in older adults, and they suggest that vitamin D supplementation may prevent such fractures—as long as it is taken in a high enough dose. (9–13)
A summary of the evidence comes from a combined analysis of 12 fracture prevention trials that included more than 40,000 elderly people, most of them women. Researchers found that high intakes of vitamin D supplements—of about 800 IU per day—reduced hip and non-spine fractures by 20 percent, while lower intakes (400 IU or less) failed to offer any fracture prevention benefit. (13)" - Comment on the IOM Vitamin D and Calcium Recommendations
For Adult Bone Health, Too Low on Vitamin D—and Too Generous on Calcium (linked in the study immediately above).
- Low vitamin D status may affect menstrual cycle length in women
- Vitamin D and Miscarriage New Study
"Vitamin D plays an important role in the modulation of the immune function (18) and oxidative stress (19) with dramatic impact on fertility ranging from poor oocyte quality, miscarriage to pregnancy complication including pre-eclampsia, preterm labor and stillbirth (16,18, 20)." - Vitamin D - Scientific review on Usage, Dosage and Side Effects
- Vitamin D status of northern indigenous people of Russia leading traditional and “modernized” way of life
- Vitamin D deficiency among northern Native Peoples: a real or apparent problem?
"There is in fact evidence that the Inuit have compensated for decreased production of vitamin D through increased conversion to its most active form and through receptors that bind more effectively. Thus, when diagnosing vitamin D deficiency in these populations, we should not use norms that were originally developed for European-descended populations who produce this vitamin more easily and have adapted accordingly." - Vitamin D and the Skin: Focus on a complex relationship: A review
The “sunshine” vitamin is a hot topic that attracted ample attention over the past decades, specially that a considerable proportion of the worldwide population are deficient in this essential nutrient. Vitamin D was primarily acknowledged for its importance in bone formation, however; increasing evidence point to its interference with the proper function of nearly every tissue in our bodies including brain, heart, muscles, immune system and skin. Thereby its deficiency has been incriminated in a long panel of diseases including cancers, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular and neurological disorders. Its involvement in the pathogenesis of different dermatological diseases is no exception and has been the subject of much research over the recent years. In the current review, we will throw light on this highly disputed vitamin that is creating a significant concern from a dermatological perspective. Furthermore, the consequences of its deficiency on the skin will be in focus. - The relationship between sun exposure and all-cause mortality
Skin cancer and all-cause mortality (from the paper)
"Sunlight exposure and fair skin are major determinants of both skin cancer and vitamin D production. Due to similar etiology and prognosis, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are often grouped as non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC). NMSC is related to cumulative UV radiation and has a good prognosis. Cutaneous malignant melanoma (MM) is the skin cancer mainly related to increased mortality and is related to episodic overexposure to UV radiation.4 There seems to be a relationship between higher sun exposure and MM incidence but an inverse relationship to prognosis. High UV exposure increases the incidence, while low sun exposure habits/vitamin D levels have been linked to thicker, more aggressive melanomas with shorter survival times.5–7 The incidence of MM has shown the greatest increase of all cancers during the last 30 years. The disease is reported to be fatal in approximately 20% of patients. In line with these prior results, we reported that of those contracting MM, 35% of women with low sun exposure and 10% of those with the highest sun exposure habits died during the follow-up period in the MISS cohort, i.e. an eight-fold increased risk of all-cause mortality among those with low sun exposure.3 Further, when grouping women based on skin cancer status (no skin cancer, NMSC, or MM) and sun exposure habits (low sun exposure, moderate exposure, or highest exposure), women with the highest sun exposure habits contracting NMSC had the highest life expectancy, while those avoiding sun exposure and contracting MM had the lowest survival rate.3 In agreement with our findings, US Navy personnel have been reported to have a 26% reduced all-cause mortality, but a higher risk of skin cancer and a reduced risk of other internal cancers.8,9 - Study shows vitamin D3 could help heal or prevent cardiovascular damage
Malinski's team has developed unique methods and systems of measurements using nanosensors, which are about 1,000 times smaller in diameter than a human hair, to track the impacts of vitamin D3 on single endothelial cells, a vital regulatory component of the cardiovascular system. A major discovery from these studies is that vitamin D3 is a powerful stimulator of nitric oxide (NO), which is a major signaling molecule in the regulation of blood flow and the prevention of the formation of clots in the cardiovasculature. Additionally, vitamin D3 significantly reduced the level of oxidative stress in the cardiovascular system.
Most importantly, these studies show that treatment with vitamin D3 can significantly restore the damage to the cardiovascular system caused by several diseases, including hypertension, atherosclerosis, and diabetes, while also reducing the risk of heart attack. These studies, performed on cells from Caucasian Americans and African Americans, yielded similar results for both ethnic groups.
"There are not many, if any, known systems which can be used to restore cardiovascular endothelial cells which are already damaged, and vitamin D3 can do it," Malinski said. "This is a very inexpensive solution to repair the cardiovascular system. We don't have to develop a new drug. We already have it." - OVERWHELMING PROOF THAT VITAMIN D3 DEFICIENCY CAUSES MOST HUMAN DISEASES
Website By Jeff Bowles - Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and subsequent risk of total and site specific cancers in Japanese population
Conclusions: In this large prospective study, higher vitamin D concentration was associated with lower risk of total cancer. These findings support the hypothesis that vitamin D has protective effects against cancers at many sites. - Low magnesium levels make vitamin D ineffective
Vitamin D can't be metabolized without sufficient magnesium levels, meaning Vitamin D remains stored and inactive for as many as 50 percent of Americans. In addition, Vitamin D supplements can increase a person's calcium and phosphate levels even while they remain Vitamin D deficient. People may suffer from vascular calcification if their magnesium levels aren't high enough to prevent the complication. - The vitamin D–antimicrobial peptide pathway and its role in protection against infection
The recent discovery that vitamin D induces antimicrobial peptide gene expression explains, in part, the ‘antibiotic’ effect of vitamin D and has greatly renewed interest in the ability of vitamin D to improve immune function. Subsequent work indicates that this regulation is biologically important for the response of the innate immune system to wounds and infection and that deficiency may lead to suboptimal responses toward bacterial and viral infections - Vitamins D3 and K2 – The Dynamic Duo - by Ron Hunninghake, MD
"The correct understanding is that vitamin K, through a chemical step called carboxylation, REGULATES and balances the coagulation system as a whole. Keep in mind that the coagulation system stands ready to CLOT if you are hemorrhaging to death, but it must also PREVENT THE CLOT if there are no lacerations or bleeding points. The eight proteins counter-regulate one another in this balancing act. Vitamin K is needed for this amazing feat.
Carboxylation of osteocalcin is another regulation feat of vitamin K which keeps bones properly mineralized with a strong protein matrix. Activated osteocalcin also stimulates adiponectin, a potent fat metabolism stimulator which helps people maintain normal weight. It is believed that all the antibiotics used in animal feed lots these days are finding their way into consumer’s guts where the beneficial bacteria that convert vitamin K into its active form are being badly disrupted. (Hence, low vitamin K in the body may be a contributing factor in the modern obesity epidemic!)
Activation of the vascular GMP protein is crucial in preventing calcification of coronary and carotid arteries. This explains the 50+% reduction in heart disease in regular vitamin K users. This same protein may also prevent bone spurs. Vitamin K is thus helping us age better with “hard bones and soft arteries”…not the other way around.
Finally, like vitamin D3, strong evidence demonstrates vitamin K’s amazing ability to reduce cancer risk. For example, men taking vitamin K2 mk7 (a naturally occurring long acting form of K2) at 45 mcg a day can statistically reduce their risk of prostate cancer by 60%! That is just one of many cancer risks that are reduced significantly by regular K2 ingestion.
As we explore the healing power of higher doses of vitamin D3 at the Riordan Clinic, we have found it prudent to partner the safety and effectiveness of this dynamic duo. For every 5,000–10,000 units of D3 being recommended and tested for, we are recommending 100 mcg of K2 mk7 to be sure and prevent the inappropriate calcification that higher doses of D3 alone could cause." - Vitamin D Wiki
Want to know more about a particular condition and see if it has an association with vitamin D status - here are links to many studies about all that. - Jeffrey Dasch MD's site on Vitamin D
A site with more information and links regarding the efficacy of vitamin D - Can Vitamin D Cure Depression?
Vitamin D insufficiency (≤20 ng/mL) has been associated with depression. If your depression is severe, you are more likely to benefit from correcting an insufficiency. If your levels of vitamin D are sufficient, however, then whether your depression is severe or not, supplementation isn’t likely to help. - Study shows magnesium optimizes vitamin D status
"A randomized trial by Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center researchers indicates that magnesium optimizes vitamin D status, raising it in people with deficient levels and lowering it in people with high levels." (Study in link below) - Magnesium status and supplementation influence vitamin D status and metabolism: results from a randomized trial
- Vitamin D and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease
"Our results confirm that vitamin D deficiency is associated with a substantially increased risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer disease. This adds to the ongoing debate about the role of vitamin D in nonskeletal conditions." - Role of Magnesium in Vitamin D Activation and Function
"Nutrients usually act in a coordinated manner in the body. Intestinal absorption and subsequent metabolism of a particular nutrient, to a certain extent, is dependent on the availability of other nutrients. Magnesium and vitamin D are 2 essential nutrients that are necessary for the physiologic functions of various organs. Magnesium assists in the activation of vitamin D, which helps regulate calcium and phosphate homeostasis to influence the growth and maintenance of bones. All of the enzymes that metabolize vitamin D seem to require magnesium, which acts as a cofactor in the enzymatic reactions in the liver and kidneys. Deficiency in either of these nutrients is reported to be associated with various disorders, such as skeletal deformities, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome. It is therefore essential to ensure that the recommended amount of magnesium is consumed to obtain the optimal benefits of vitamin D" - Vitamin D Status in Children with Leukemia
"Subnormal 25-OHD levels are common in pediatric patients with leukemia already at the time of diagnosis. In younger children with leukemia 25-OHD level <50 nmol/L is associated with inferior survival." - The Role of Cathelicidin LL-37 in Cancer Development
"Having cholecalciferol in serum in a free and available form all the time ensures immune function can increase the production of cathelicidin whenever required" - Edward Hutchinson
1) Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on vitamin D status and cathelicidin levels in sepsis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial
"High-dose cholecalciferol supplementation rapidly and safely improves 25OHD and bioavailable 25OHD levels in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Changes in bioavailable 25OHD are associated with concomitant increases in circulating LL-37 levels. Larger trials are needed to verify these findings and to assess whether optimizing vitamin D status improves sepsis-related clinical outcomes."
2) Administration of oral vitamin D induces cathelicidin production in atopic individuals
"Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to increased rates of multiple cancers, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and hypertension.8 We believe our study has shown that supplementation of oral vitamin D can result in correction of defects in cathelicidins in the innate immune system of atopic subjects.
3) Positive correlation between circulating cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (hCAP18/LL-37) and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in healthy adults
We conclude that plasma hCAP18 levels correlate with serum 25(OH)D levels in subjects with concentrations of 25(OH)D ≤ 32 ng/ml as opposed to those with concentrations > 32 ng/ml and that vitamin D status may regulate systemic levels of hCAP18/LL-37. - Lack of sun causing rickets in Australian children
Despite living in one the sunniest places on the planet, hundreds of children have been diagnosed with vitamin D deficiency rickets, a preventable bone disease that can cause delayed growth and skeletal deformities. - Incidence of vitamin D deficiency rickets among Australian children: an Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit study
- Vitamin D deficiency linked to MS
"Professor Richard Mellanby, of the University of Edinburgh's Centre for Inflammation Research, said: "Low vitamin D status has long been implicated as a significant risk factor for the development of several autoimmune diseases.
"Our study reveals one way in which vitamin D metabolites can dramatically influence the immune system."" - Top UK scientist urges people to take vitamin D supplements
Geneticist Steve Jones, formerly a sceptic, says case for doing so is overwhelming
“Children today spend an hour a day less outside than they did 10 years ago. That’s the smartphone and the tablet situation. Scottish children spend less time in the sun than any other children in the world.”
He said the bone disease rickets, which doctors thought they had eliminated from Britain in the 1950s, was a real issue today. “Rickets is coming back and rickets is coming back at some speed. It is coming back because of a shift in human behaviour which we never thought would happen,” he said.
Jones said the benefits of sunshine and vitamin D could be felt across a range of health areas including obesity, mood and blood pressure. He cited multiple sclerosis, which is most common in northern Canada and almost unheard of in tropical countries. In the UK, levels are higher in Scotland than England.
Scotland gets the least sunshine in the UK and Scottish men have a life expectancy two years less than men in England and Wales, he said. “Scotland is still the sick man of Europe. The Scots are the palest people in the world … and that’s because their entire body systems are crying out for vitamin D.”
Jones is professor of genetics at University College London and is considered one of the finest science communicators of his generation. He was in Hay talking about his new book, Here Comes the Sun.
Jones told the audience that vitamin D had many unexpected effects on the body, including the immune system. “It can help tackle infectious disease, it changes mood, if you have a shortage you’re more likely to get kidney disease … it is really, really important stuff. The evidence that the shortage of sunlight has drastic effects on health is overwhelming.” - Occupational sunlight exposure and melanoma in the U.S. Navy
"Abstract
Melanoma is the second most common cancer, after testicular cancer, in males in the U.S. Navy. A wide range of occupations with varying exposures to sunlight and other possible etiologic agents are present in the Navy. Person-years at risk and cases of malignant melanoma were ascertained using computerized service history and inpatient hospitalization files maintained at the Naval Health Research Center. A total of 176 confirmed cases of melanoma were identified in active-duty white male enlisted Navy personnel during 1974-1984. Risk of melanoma was determined for individual occupations and for occupations grouped by review of job descriptions into three categories of sunlight exposure: (1) indoor, (2) outdoor, or (3) indoor and outdoor. Compared with the U.S. civilian population, personnel in indoor occupations had a higher age-adjusted incidence rate of melanoma, i.e., 10.6 per 100,000 (p = .06). Persons who worked in occupations that required spending time both indoors and outdoors had the lowest rate, i.e., 7.0 per 100,000 (p = .06). Incidence rates of melanoma were higher on the trunk than on the more commonly sunlight-exposed head and arms. Two single occupations were found to have elevated rates of melanoma: (1) aircrew survival equipmentman, SIR = 6.8 (p less than .05); and (2) engineman, SIR = 2.8 (p less than .05). However, there were no cases of melanoma or no excess risk in occupations with similar job descriptions. Findings on the anatomical site of melanoma from this study suggest a protective role for brief, regular exposure to sunlight and fit with recent laboratory studies that have shown vitamin D to suppress growth of malignant melanoma cells in tissue culture. A mechanism is proposed in which vitamin D inhibits previously initiated melanomas from becoming clinically apparent." - The Vitamin D Levels of the Hadzabe and the Maasai: An Important Study That Flew Under the Radar
"Deep down, in our genes, we’re all Africans. Given that so much of our evolutionary journey took place in a natural environment close to equator, it makes sense to look to populations that still live under such conditions for clues as to what constitutes physiological normality and conditioning from an evolutionary point of view. With respects to the all-important hormone referred to as vitamin D, which plays a critical role in processes related to immune function, bone homeostasis, and the workings of the mind, among other things, it’s been shown that traditional African populations have a mean 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration of about 115 nmol/l, which far surpasses that of western populations. This value matches the value that has been shown to relate to optimal health and protection against disease in certain studies, and hence, may serve as a basis for crafting vitamin D-related research and recommendations." - Circulating Vitamin D3 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D in Humans: An Important Tool to Define Adequate Nutritional Vitamin D Status
"What is a normal circulating level of 25(OH)D that is sufficient to meet all physiological needs, not simply skeletal requirements in humans? In the past, this was addressed by simply sampling a diverse population of subjects who were asymptomatic for disease, measuring circulating 25(OH)D, and plotting the data using a Gaussian distribution. This approach yields normative data that are used to assess circulating 25(OH)D in that population. This is how Haddad and Chyu (1) performed their assessment of 25(OH)D status more than thirty-five years ago. They referred to their normal, asymptomatic volunteers as the normal population for circulating 25(OH)D levels. Their study also presented a group of lifeguards that had circulating 25(OH)D levels 2.5 times that of the “normals.” Countless similar studies have been performed during the ensuing decades, reiterating the same conclusion. We, however, interpret the original Haddad data differently: we suggest that the 25(OH)D levels in the sun-replete lifeguards are normal and the “normals” actually exhibit varying degrees of vitamin D deficiency.
How nutritional vitamin D deficiency is defined is a key to developing a coherent supplement policy that meets the needs of all humans. Recently, inadequate circulating 25(OH)D levels have been linked to biomarkers, including skeletal density (2–4), intestinal calcium absorption (5), secondary hyperparathyroidism (6–10), insulin secretion (11, 12), and innate immune response (13). These markers all are useful in identifying nutritional vitamin D deficiency; however, the link between 25(OH)D and vitamin D—when available at adequate concentration, remains unknown and could prove to be another important piece in understanding vitamin D metabolism. We sought to investigate this question of how 25(OH)D would respond if adequate substrate, namely vitamin D3, was always present. Thus, for this project, we studied two groups of subjects, one from a sun-rich environment and the other from a high-dose vitamin D3 supplementation study, the results of which are presented here." - Vitamin D Toxicity–A Clinical Perspective
In which the potential for toxicity is discussed with particular relevance for people with sarcoidosis and other granulomatous diseases. - Role of Magnesium in Vitamin D Activation and Function
Important to ensure adequate magnesium intake.
"Magnesium homeostasis is maintained by the delicate interactions of the intestine, bone, and kidneys. Magnesium is an essential cofactor for vitamin D synthesis and activation and, in turn, can increase intestinal absorption of magnesium and establish a feed-forward loop to maintain its homeostasis. Dysregulation in either of these nutrients can be associated with various disorders, including skeletal deformities, cardiovascular disorders, and metabolic syndrome." - Vitamin D3 and K2 and their potential contribution to reducing the COVID-19 mortality rate
Recent COVID-19-related data evaluation showed indications that a high 25(OH)D blood serum level might have an impact on the mortality rate of coronavirus patients. Even though ethical issues might arise (Muthuswamy, 2013), the paper’s hypothesis requires clinical randomized trials to verify the circumstantial evidence. This publication illustrated the metabolic mechanisms behind that observed phenomenon. It is highly suggested to also consider K2 and magnesium intake to avoid unintended long-term side-effects such as arteriosclerosis and osteoporosis. - Vitamin D and brain health: an observational and Mendelian randomization study - 22 April, 2022
Low vitamin D status was associated with neuroimaging outcomes and the risks of dementia and stroke even after extensive covariate adjustment. MR analyses support a causal effect of vitamin D deficiency on dementia but not on stroke risk. - Could Vitamin D ward off suicide?
Suicide is a serious public health risk and the 12th leading cause of death in the U.S. A 2023 study of U.S. veterans found those with vitamin D deficiency who were prescribed vitamin D had a 64% lower risk of suicide when compared to those who didn't take a supplement
This adds to the growing body of evidence that insufficiency or deficiency is linked to depression; other nutrients found to improve mental health include vitamin B6 and magnesium
Consuming refined sugar and a high carbohydrate diet may also increase your risk of depression as sugar primarily drives chronic inflammation, which is linked to depression. A 2019 study demonstrated that avoiding sugar, soft drinks, processed meat and refined carbohydrates lowered levels of depression and anger
Low levels of vitamin D also increase your risk of all-cause mortality by 25%, cancer mortality by 16% and lung-related illness by 96%. I firmly believe the data show that optimizing vitamin D can help prevent COVID and lower your risk of severe symptoms
| |||||||
Skin cancer and all-cause mortality (from the paper)
"Sunlight exposure and fair skin are major determinants of both skin cancer and vitamin D production. Due to similar etiology and prognosis, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are often grouped as non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC). NMSC is related to cumulative UV radiation and has a good prognosis. Cutaneous malignant melanoma (MM) is the skin cancer mainly related to increased mortality and is related to episodic overexposure to UV radiation. There seems to be a relationship between higher sun exposure and MM incidence but an inverse relationship to prognosis. High UV exposure increases the incidence, while low sun exposure habits/vitamin D levels have been linked to thicker, more aggressive melanomas with shorter survival times. The incidence of MM has shown the greatest increase of all cancers during the last 30 years. The disease is reported to be fatal in approximately 20% of patients. In line with these prior results, we reported that of those contracting MM, 35% of women with low sun exposure and 10% of those with the highest sun exposure habits died during the follow-up period in the MISS cohort, i.e. an eight-fold increased risk of all-cause mortality among those with low sun exposure. Further, when grouping women based on skin cancer status (no skin cancer, NMSC, or MM) and sun exposure habits (low sun exposure, moderate exposure, or highest exposure), women with the highest sun exposure habits contracting NMSC had the highest life expectancy, while those avoiding sun exposure and contracting MM had the lowest survival rate. In agreement with our findings, US Navy personnel have been reported to have a 26% reduced all-cause mortality, but a higher risk of skin cancer and a reduced risk of other internal cancers.
"Sunlight exposure and fair skin are major determinants of both skin cancer and vitamin D production. Due to similar etiology and prognosis, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are often grouped as non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC). NMSC is related to cumulative UV radiation and has a good prognosis. Cutaneous malignant melanoma (MM) is the skin cancer mainly related to increased mortality and is related to episodic overexposure to UV radiation. There seems to be a relationship between higher sun exposure and MM incidence but an inverse relationship to prognosis. High UV exposure increases the incidence, while low sun exposure habits/vitamin D levels have been linked to thicker, more aggressive melanomas with shorter survival times. The incidence of MM has shown the greatest increase of all cancers during the last 30 years. The disease is reported to be fatal in approximately 20% of patients. In line with these prior results, we reported that of those contracting MM, 35% of women with low sun exposure and 10% of those with the highest sun exposure habits died during the follow-up period in the MISS cohort, i.e. an eight-fold increased risk of all-cause mortality among those with low sun exposure. Further, when grouping women based on skin cancer status (no skin cancer, NMSC, or MM) and sun exposure habits (low sun exposure, moderate exposure, or highest exposure), women with the highest sun exposure habits contracting NMSC had the highest life expectancy, while those avoiding sun exposure and contracting MM had the lowest survival rate. In agreement with our findings, US Navy personnel have been reported to have a 26% reduced all-cause mortality, but a higher risk of skin cancer and a reduced risk of other internal cancers.
|
New Zealand author, Ian Wishart, has researched and written a book on vitamin D
"IF YOU STILL HAVE A HEARTBEAT, THIS BOOK IS DIRECTLY RELEVANT TO YOU Vitamin D is the hottest development in medical science, and in this compelling new book, bestselling author Ian Wishart brings together the most up to date science on vitamin D and how it could well save your life. Cancer? Up to a 77% reduction in risk of developing it if you take this vitamin. Heart disease? The same kind of reduction. Did you know that autism, mental illness and multiple sclerosis all appear to be affected by a lack of vitamin D during pregnancy? Did you know that ADHD and asthma appear to result from that same deficiency? The lives of every single person, including you, will be affected by the information in this book. More than 300 scientific studies are cited, making this an ideal reference book for the public and medical professionals alike. CONDITIONS COVERED: Asthma, Autism, Allergies, Alzheimer's, Breast Cancer, Bowel Cancer, Skin Cancer, Melanoma, Heart Disease, Stroke, Colds, Flu Pandemics, Crohn's Disease, Mental Illness, Diabetes, Tuberculosis, Multiple Sclerosis, Depression, ADHD, Pregnancy, Infertility, Hospital Superbugs and more... |
|
Journalism Bias at Its Best
Just in - a couple of rather slanted views on vitamin D from the NY Times - who think that the $15 a year I spend is helping support a research grant
Just in - a couple of rather slanted views on vitamin D from the NY Times - who think that the $15 a year I spend is helping support a research grant
- Vitamin D, the Sunshine Supplement, Has Shadowy Money Behind It
- Why Are So Many People Popping Vitamin D?
- Kaiser Health News wrote a damning article about Dr. Holick and Vitamin D, NYT published it – Aug 2018
Finally, the New York Times published another story on vitamin D! During the last 12 months, scientists from around the world published 4,620 new vitamin D peer-reviewed vitamin D studies, adding to the National Library of Medicine’s (NLM)’s 77,322 current vitamin D holdings. During the same year, the Times ran one story about D, also a hit piece. Are any of those 77,322 studies of interest to the Times? What about vitamin D and the Kakapo, a large nocturnal, forest dwelling and flightless parrot native to New Zealand, and possible extinction? Or, vitamin D as the only compound tested that helps prevent tissue damage in a mustard gas attack? Better yet - the Times, Szabo and your 4 anti-D experts will like this one, vitamin D is one the most commonly used rat poisons in the US.
The sun goes down on Vitamin D: why I changed my mind about this celebrated supplement
Article by Dr Tim Spector in The Conversation describing why he is now against vitamin D supplementation - however he seems to cherry pick articles and doesn't think about why some dosing regimens show poor or negative results.
Article by Dr Tim Spector in The Conversation describing why he is now against vitamin D supplementation - however he seems to cherry pick articles and doesn't think about why some dosing regimens show poor or negative results.
- "The usual prescribed dose in most countries is 800 to 1,000 units per day (so 24,000-30,000 units per month). However, two randomised trials found that at around 40,000 to 60,000 units per month Vitamin D effectively became a dangerous substance.
"One study involving over 2,000 elderly Australians, which was largely ignored at the time, and the one just published found that patients given high doses of vitamin D or those on lower doses that increased vitamin D blood levels within the optimal range (as defined by bone specialists) had a 20-30% increased rate of fractures and falls compared to those on low doses or who failed to reach “optimal blood levels”.
Bottom Line
- The human species evolved for much of the time near the equator.
(Serum 25(OH)D levels of 175 - 200 nmol/l are within 'normal' range.) - Our daily uptake of vitamin D from sun exposure can be up to 20,000IU before UV starts breaking it down again.
(Our physiological Upper Tolerable Limit?) - Healthy adult males can utilize 3000-5000 IU daily for normal metabolic needs.
- Stored vitamin D becomes unavailable for soft tissue use after about 24 hours and for bone use after about 2 weeks.
- Incidence of many cancers increases the further away people live from the equator.
- It is possible to raise serum 25(OH)D by taking supplemental D3 capsules
- Please read in conjunction with the page on vitamin K - IMPORTANT!
These are the D3 supplements I've found to be cost-effective
...and the K2